How to identify fake users and bots in Web3 advertising

The decentralized web is growing quickly, but this has also brought a big hidden risk: a bot epidemic that could destroy the very foundation of digital growth. In 2026, fake users and automated traffic are more than just simple scripts. They have grown into complex systems powered by Agentic AI and Sophisticated Invalid Traffic (SIVT). For Web3 advertisers, founders, and marketers, being able to tell the difference between real human engagement and fake inflation is what separates building a long-lasting protocol from paying for unsustainable metrics.
The biggest problem with Web3 marketing is that it often focuses on hype instead of getting real users. According to data from Visa and Allium, nearly 90% of stablecoin transactions were not made by people. CryptoSlam data shows that more than 40% of trading on networks like Ethereum is also related to wash trading. These numbers show that tens of billions of dollars in fake volume were used to change people’s minds and waste marketing money.
Common signs of fake users and bot activity
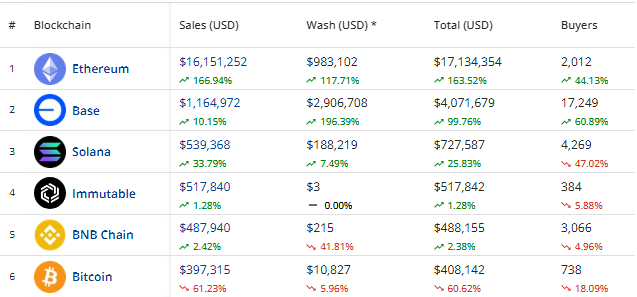
To find fake traffic in the current environment, you need to use a layered approach. Advertisers need to look beyond basic metrics to find behavioral and technical problems that scripts can’t be easily copied without spending a lot of money. As Nick Morley, CEO of Lunio, noted:
“Invalid traffic is one of the biggest invisible drains on digital performance… When that noisy and polluted data feeds into automated bidding and targeting algorithms, the waste compounds even further.”
| Category | Warning Sign | Description |
| Behavioral | High CTR / Low Conversion | Massive click volume but zero meaningful post-click action. |
| Behavioral | Abnormal session duration | Users bounce in 1-2 seconds or stay for an unnaturally fixed time. |
| Behavioral | Irregular traffic spikes | Surges in activity during odd hours or from non-target regions. |
| Behavioral | Repetitive interaction paths | Multiple users follow identical navigation sequences. |
| Behavioral | Lead quality issues | Form submissions containing gibberish or disposable email addresses. |
| Technical | Data center IP addresses | Traffic originating from cloud servers like AWS or DigitalOcean. |
| Technical | Mismatched device fingerprints | Discrepancies between the reported browser and the actual device resolution. |
| Technical | Headless browser signatures | Traces of browsers running without a graphical user interface. |
| Technical | Inhuman interaction speed | Clicks or form fills occurring in milliseconds. |
| Technical | Legacy system exploitation | High traffic from outdated operating systems like Windows 8. |
High CTR with negligible conversions
An ad campaign that gets a lot of clicks but not a lot of conversions is a classic red flag. This is usually a sign that a click farm or an automated script is using up a competitor’s budget to please the algorithms of an ad network. By 2026, bots have become highly effective at mimicking human behavior; they use randomized timing and simulated scrolling to bypass basic filters. However, they still don’t turn into users who are economically active.
Abnormal session duration
People who are real don’t always follow the same path. A fake user usually does one of two things: they either leave a page within 1-2 seconds of loading it or stay for a perfectly consistent amount of time (like exactly 60 seconds) before ending the session. You can see these patterns that are too consistent with normal analytics tools like GA4.
Irregular traffic spikes
If there are sudden spikes in activity at 3:00 AM in the time zone of your target market or from areas outside of your main focus, this is a strong sign of botnets. Advanced bots use residential proxies to look like home connections, but the timing of their actions often gives away that they are automated.
Repetitive interaction paths
When a lot of people do the same thing in the same order, like clicking a button without moving the mouse or scrolling, it means that the automation was scripted. People don’t always do things in a straight line when they interact with each other. For example, they might stop to read something or hover over a picture.
Lead quality issues
A lot of sign-ups that use temporary email addresses or have junk data in form fields are a clear sign of Web3 bot activity. We are seeing an increasing trend of scammers using LLMs to bypass form filters with answers that sound like they came from a real person. This can make it harder to find fraud until the sales team realizes that the leads are fake.
On-chain indicators vs off-chain signals
Advertisers need to combine on-chain indicators (which are unchangeable proof of identity and economic history) with off-chain behavioral signals to really verify a user in Web3. Using only one makes you blind to things that advanced AI-powered botnets can take advantage of.
On-chain data gives a hard signal of the economy’s legitimacy.
- Wallet age & first usage: A wallet that has been around for years is much more reliable than a burner wallet that was made just minutes before someone clicked on an ad. Use tools like Dune Analytics or Nansen to check.
- Transaction history: Real users show consistent, non-repetitive behavior across different protocols. Bots usually do the same thing over and over again, like only clicking on a link that leads to an ad.
- Economic activity (Gas spent): Since every action on the blockchain costs gas, a user’s past gas spending serves as proof of work for their legitimacy.
Off-chain signals show the “how” and “why” of what users do.
- Dwell time: Platforms like LinkedIn and Meta now measure exactly how long a user views content. Bots usually don’t stay on a page for very long.
- Funnel drop-offs: A clear sign of bot activity is a 100% drop-off rate between the sign-up page and the second session.
- Session behavior: In 2026, AI-powered pattern recognition can pick out the erratic, non-linear scrolling and pausing that real human readers do.
Combining these signals is the best way to find a fake user agent. For instance, if you see a user with a high dwell time off-chain (a real person signal) and then check that they have a multi-year-old wallet with a variety of transactions on-chain (economic legitimacy), you can be sure that they are who they say they are.
How bots manipulate Web3 ad metrics
In 2026, bot operations distort every stage of the marketing funnel to satisfy artificial KPIs.
- CTR manipulation: Bots make a lot of clicks to make low-quality platforms look like they’re doing well.
- CPA distortion: Scammers use lead bots to fill out forms, which makes the Cost Per Acquisition look lower on paper. This tricks advertisers into spending more money on fake channels.
- App installs: Malicious code can use techniques like SDK spoofing to make it look like a legitimate app install without actually downloading anything. Click injection is another risk. This happens when a listener app sees that an install is about to happen and sends a fake ad click to get the referral credit.
- Wallet connections: Bots automatically make Sybil wallets to farm airdrops and community rewards. They pretend to be thousands of different users when in reality they are just one bad actor.
Tools and methods advertisers use to filter fake traffic
To keep their budgets and communities safe, serious Web3 advertisers use a Defense-in-Depth strategy.
On-chain identity and Sybil-resistance tools
It’s important to give priority to users with a Proof of Personhood. The Gitcoin Passport and Galxe Passport give users a Humanity Score based on their past on-chain activity and verified social media accounts. Advertisers can set their campaigns to only give rewards to wallets that have a score higher than a certain level.
Web3-native ad networks with built-in filtering
Advertisers are moving away from general networks and toward platforms that include blockchain auditing directly. Wallet-based targeting is possible on networks like Bitmedia, which lets you filter traffic based on a user’s on-chain portfolio (for example, only show ads to users with >0.5 ETH). This makes it much more expensive for bot operators to make a targetable profile.
Advanced SIVT and ZK-proofs
DoubleVerify and Fraudlogix are examples of enterprise-grade tools that protect against Sophisticated Invalid Traffic before a bid is made. Platforms like Rarimo also use Zero-Knowledge (ZK) Proofs to check that a user is a real person without giving away private information. This lets bot filtering that protects privacy.
Why quality traffic matters more than volume in Web3
The growth at all costs mindset of Web2 doesn’t work well in decentralized settings. When you look at the lack of organic usage in protocols, which is when you have high vanity metrics but no real life, you can see why quality traffic is more important than volume in Web3.
When a project depends on numbers that are inflated by bots, it runs three big risks:
- Damage to token launches: According to Crypto.news, as many as 70% of people who say they use them are bots. These actors “farm and dump,” which makes prices go down right after launch, which is bad for real investors.
- Erosion of governance: Bots are used in Sybil attacks to make it look like the community agrees, which can be used to steal money or change the rules.
- Destruction of trust: People will eventually find out that a community is fake, which will cause the brand to fail and users to leave.
Building a foundation of authentic engagement
Success in Web3 advertising in 2026 is defined by informed judgment and transparency. The goal is no longer just to shout the loudest, but to convert attention into trust and trust into long-term usage. By valuing user authenticity and combining rigorous on-chain and off-chain analysis, advertisers can safeguard their projects from the bot epidemic. The shift toward data-driven decisions replacing vanity metrics is the only path to unlocking mass adoption. In this new landscape, verified engagement is the reliable metric that guarantees a project’s future.


